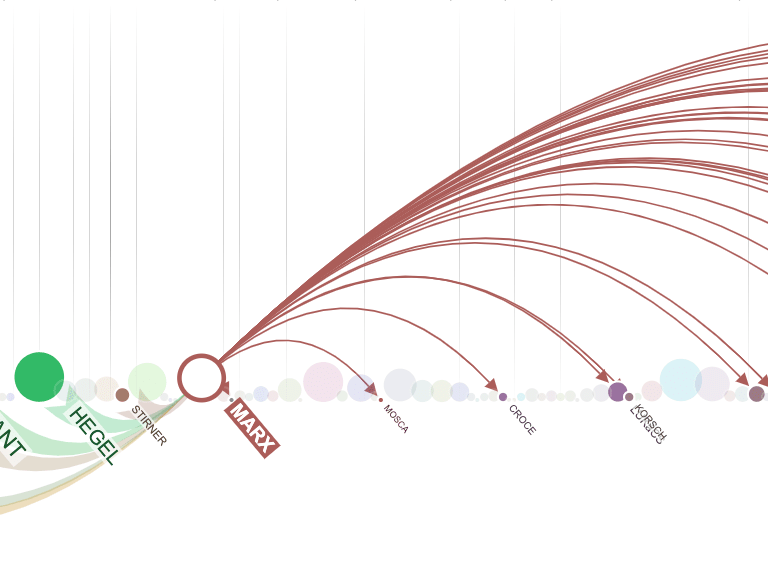
Attribute-driven positioning (fixed layouts) assigns node or edge positions according to one or more attribute values.
Optimized for small and sparse networks. Is well suited for few node attributes, particular of homogenous types.
Supports few edge attributes, but only if of homogenous types. Can be used for tasks on neighbors and networks.
Not ideal for tasks on paths, clusters, and for large, dense, layered or tree networks.