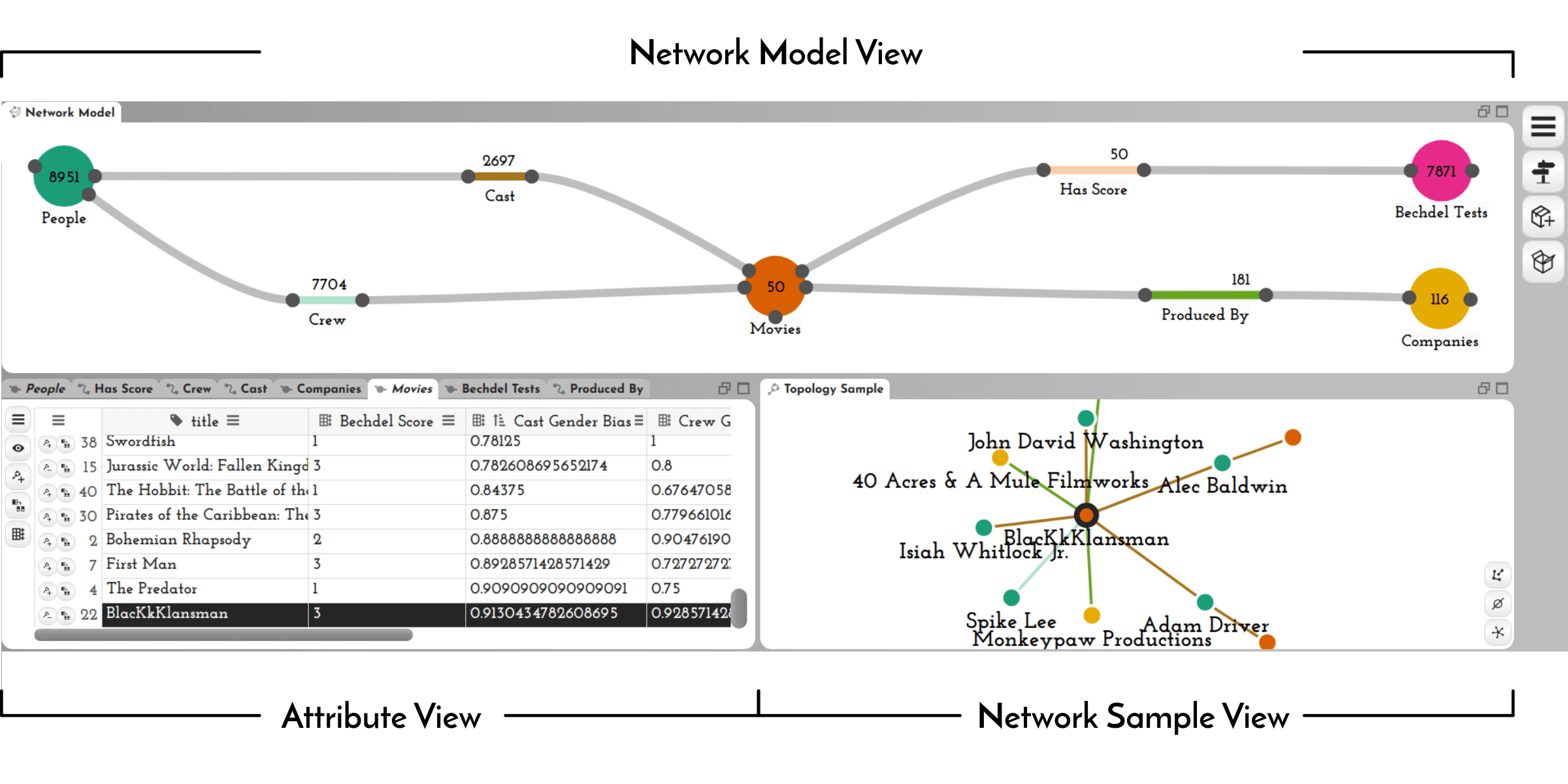
Abstract
Networks are a natural way of thinking about many datasets. The data on which a network is based, however, is rarely collected in a form that suits the analysis process, making it necessary to create and reshape networks. Data wrangling is widely acknowledged to be a critical part of the data analysis pipeline, yet interactive network wrangling has received little attention in the visualization research community. In this paper, we discuss a set of operations that are important for wrangling network datasets and introduce a visual data wrangling tool, Origraph, that enables analysts to apply these operations to their datasets. Key operations include creating a network from source data such as tables, reshaping a network by introducing new node or edge classes, filtering nodes or edges, and deriving new node or edge attributes. Our tool, Origraph, enables analysts to execute these operations with little to no programming, and to immediately visualize the results. Origraph provides views to investigate the network model, a sample of the network, and node and edge attributes. In addition, we introduce interfaces designed to aid analysts in specifying arguments for sensible network wrangling operations. We demonstrate the usefulness of Origraph in two Use Cases: first, we investigate gender bias in the film industry, and then the influence of money on the political support for the war in Yemen.
Citation
Alex Bigelow,
Carolina Nobre,
Miriah Meyer,
Alexander Lex
Origraph: Interactive Network Wrangling
IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), 81-92, doi:10.1109/VAST47406.2019.8986909, 2019.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{2019_vast_origraph,
title = {Origraph: Interactive Network Wrangling},
author = {Alex Bigelow and Carolina Nobre and Miriah Meyer and Alexander Lex},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST)},
doi = {10.1109/VAST47406.2019.8986909},
pages = {81-92},
year = {2019}
}
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Science Foundation (OAC 1835904, IIS 1350896, IIS 1751238) and by the Utah Genome Project.